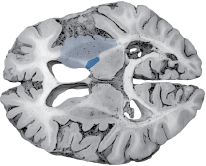
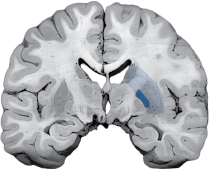
The Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) is the most common site of stroke. MCA infarcts occur in two general regions: superficial divisions and lenticulostriate branches.
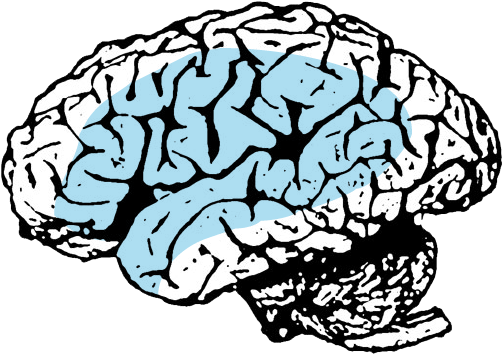
Movement of right head, neck, trunk and arm.
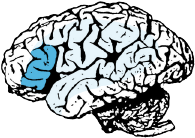
Sensation from right head, neck, trunk and arm.
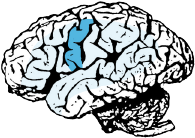
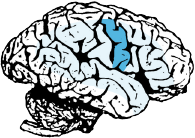
Expressive speech area.
Integration with other language areas.
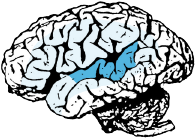
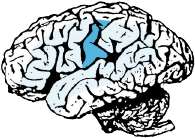
Receptive speech area.
Integration with other language areas.
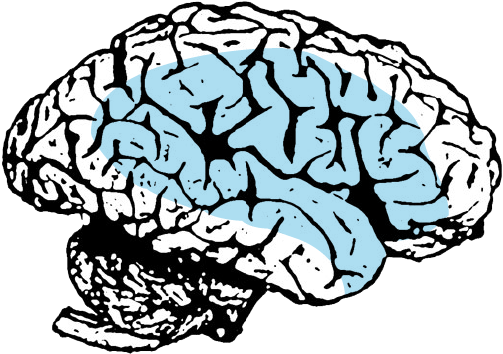
Movement of left head, neck, trunk and arm.
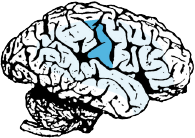
Sensation from left head, neck, trunk and arm.
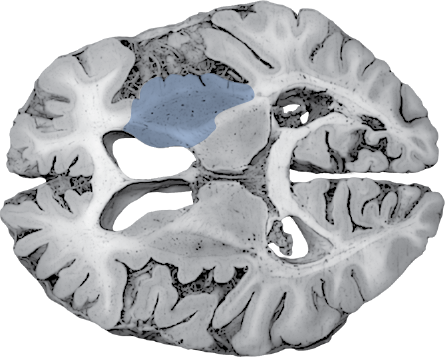
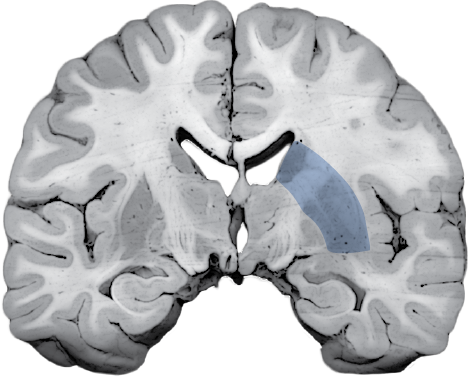
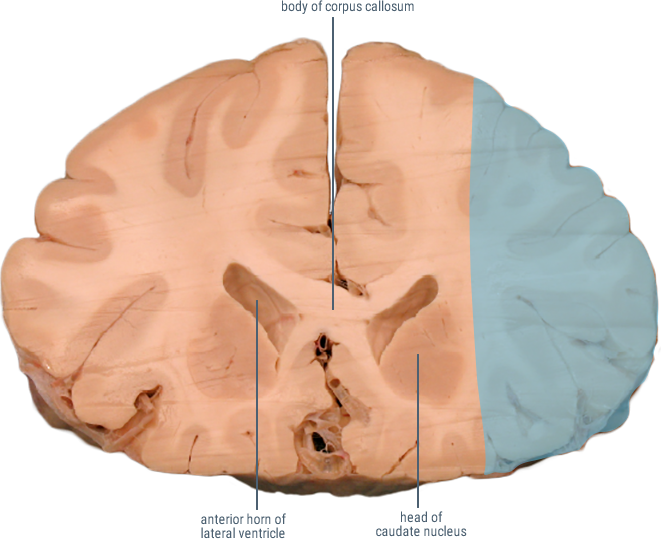
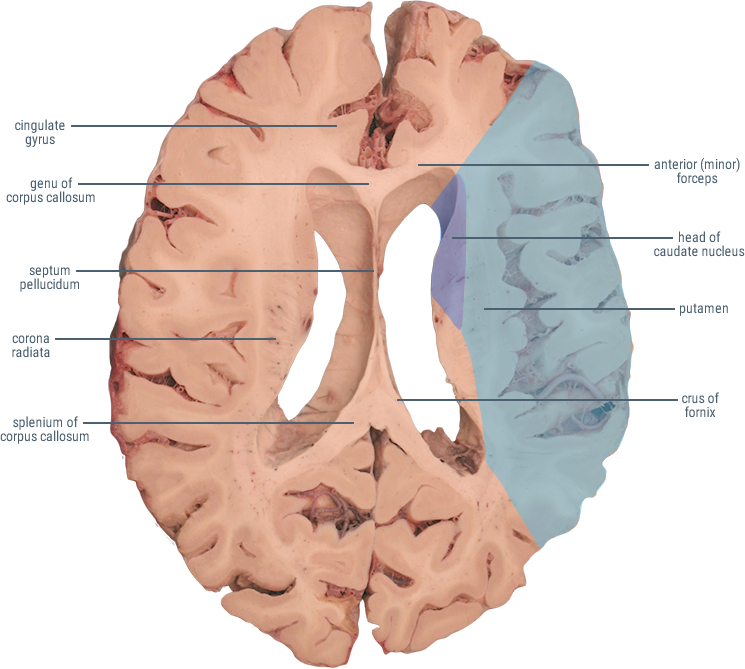
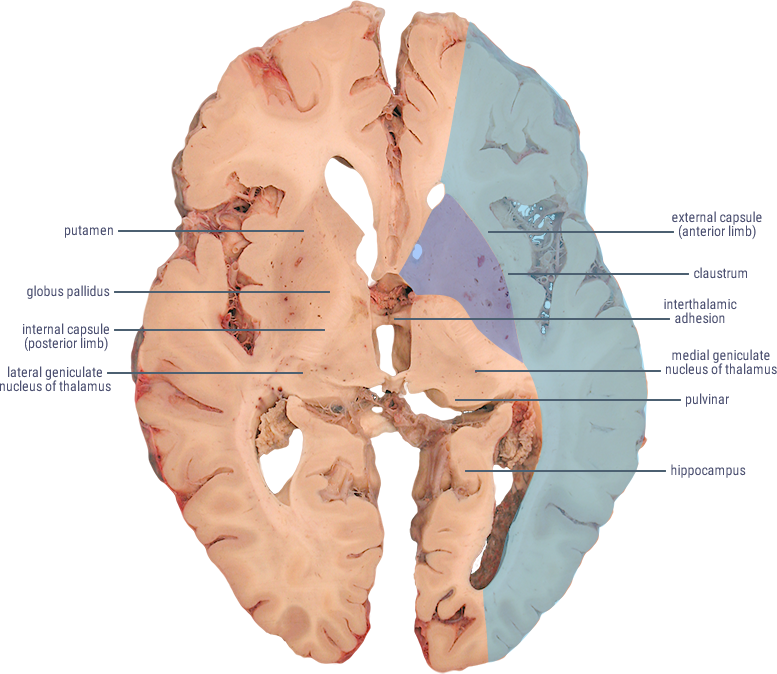
(Caudate and Putamen)
Receives cortical inputs relayed to basal ganglia.
Functions in direct and indirect pathways for initiation and control of movement.
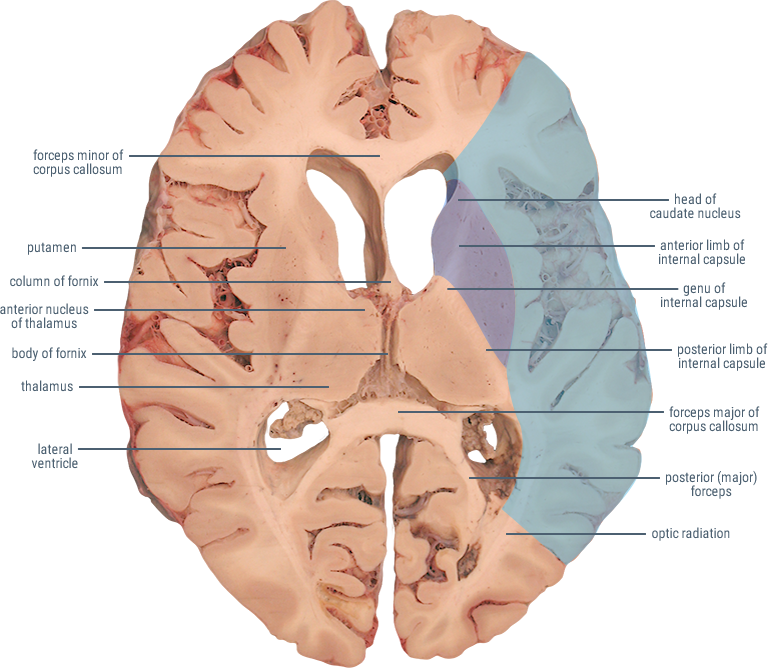
(Anterior Limb)
Contains corticopontine and thalamocortical fibers.
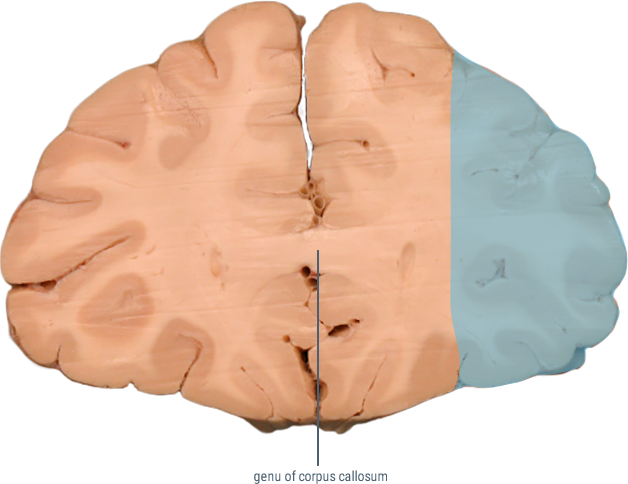
(Genu)
Contains descending fibers of the corticobulbar tract.
Site of origin of output from the basal ganglia to substantia nigra and thalamus.
Functions in direct and indirect pathways for initiation and control of movement.
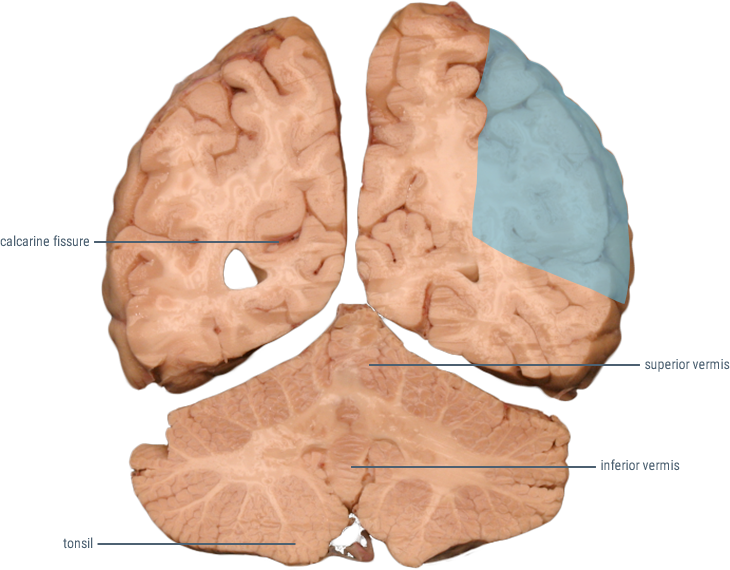
CORONAL SECTIONS
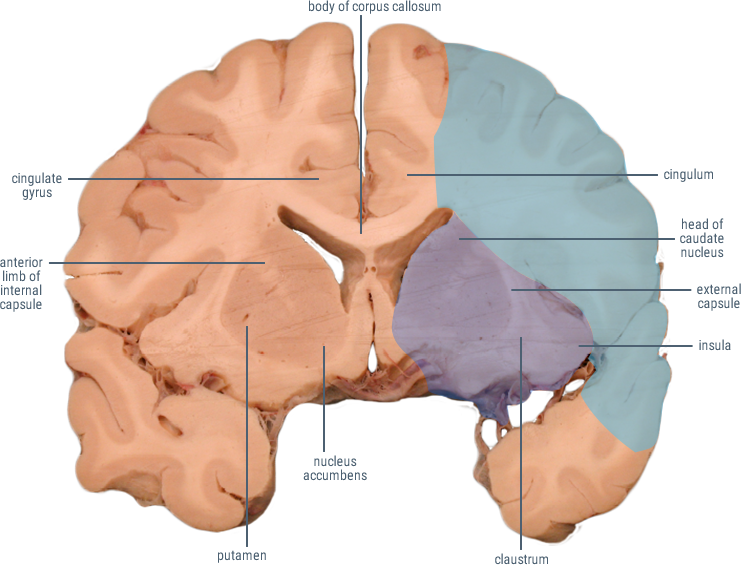
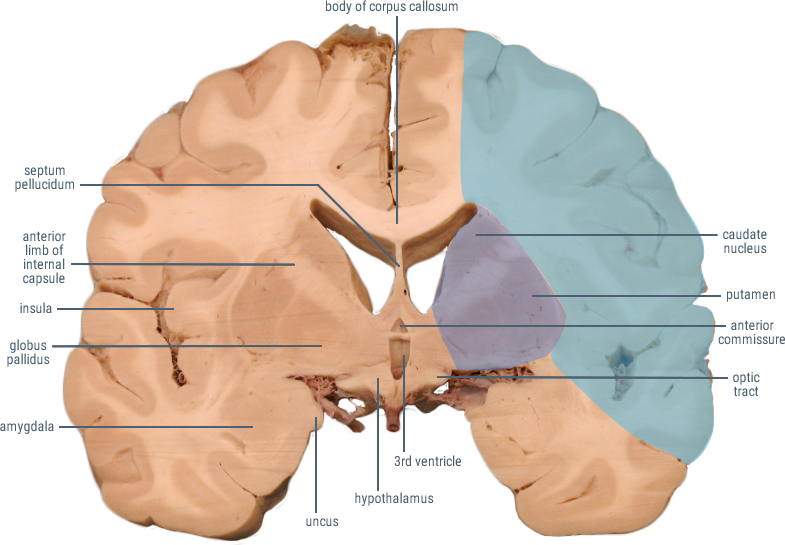
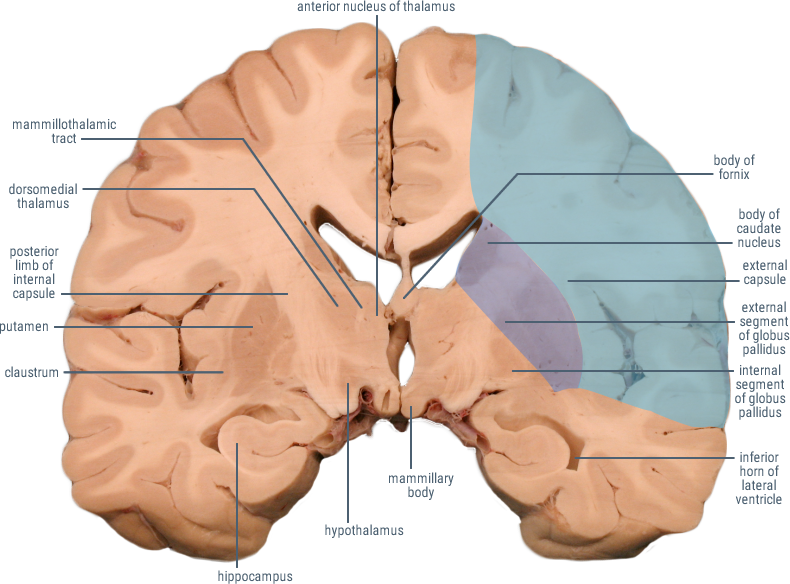
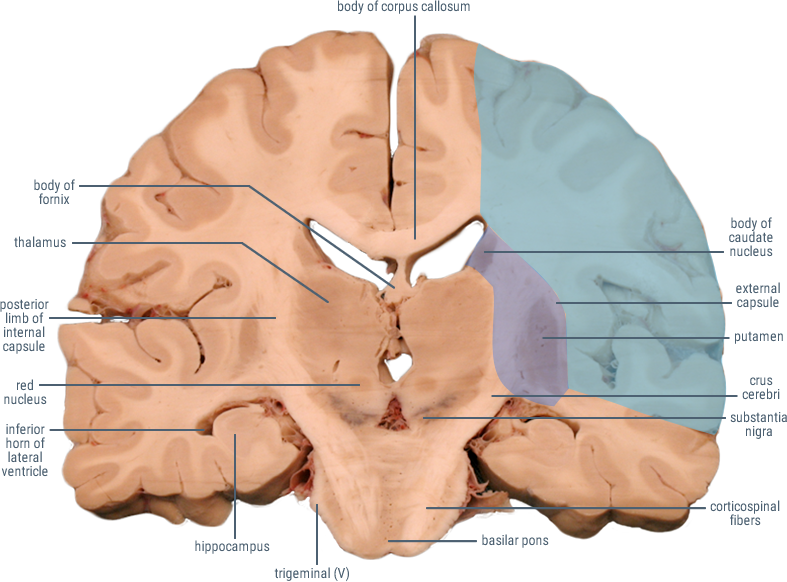
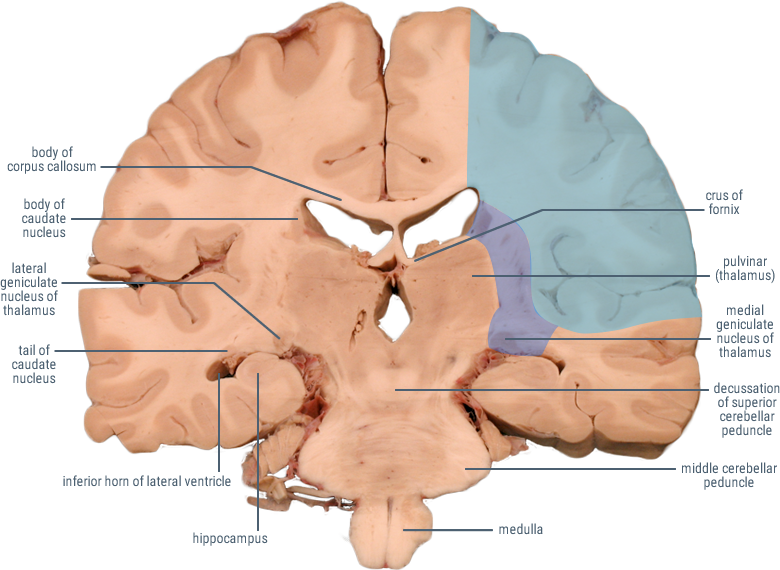
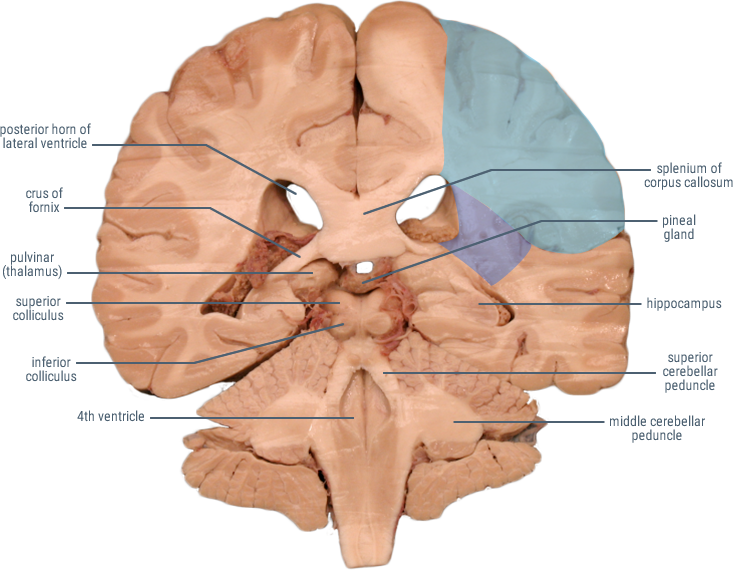
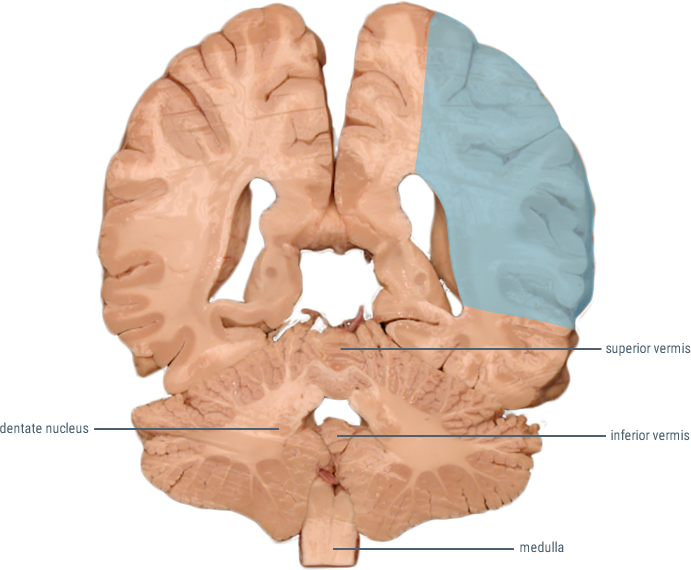
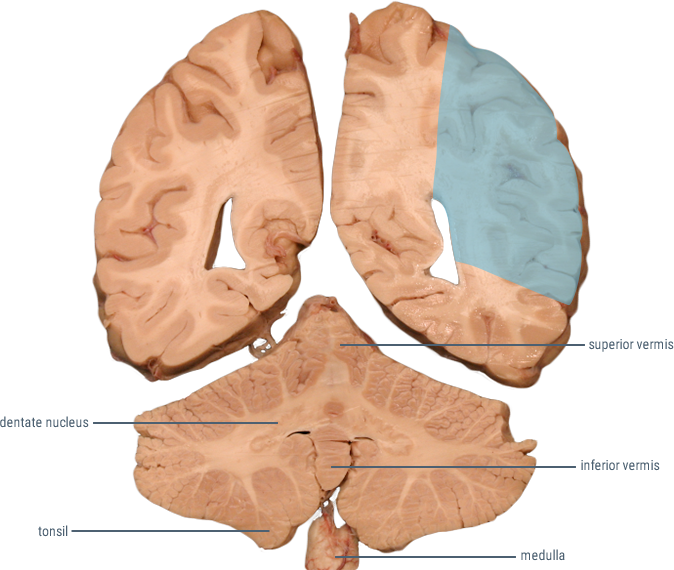
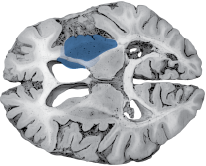
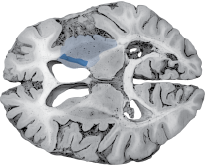
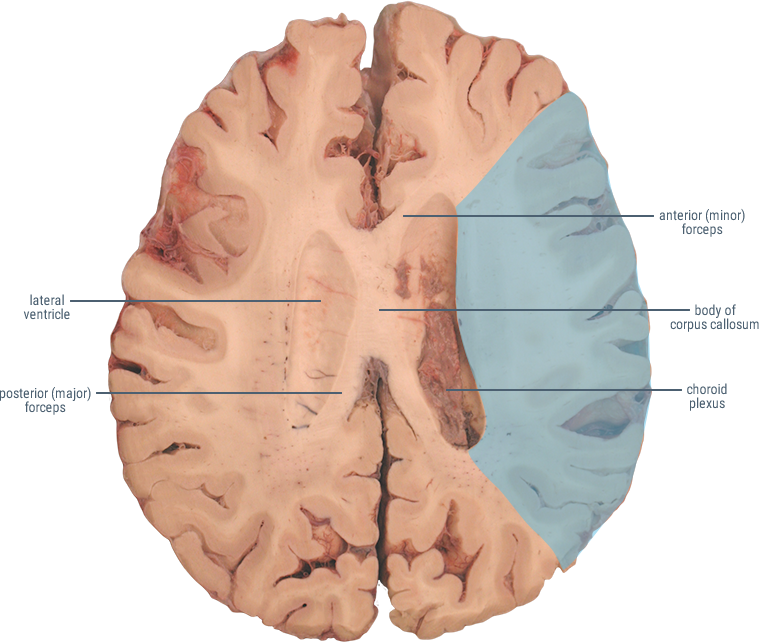
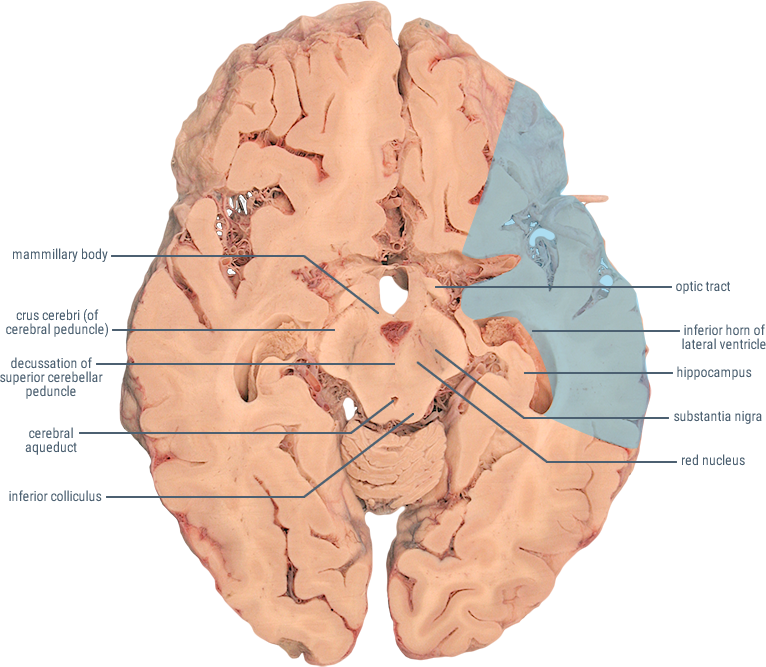
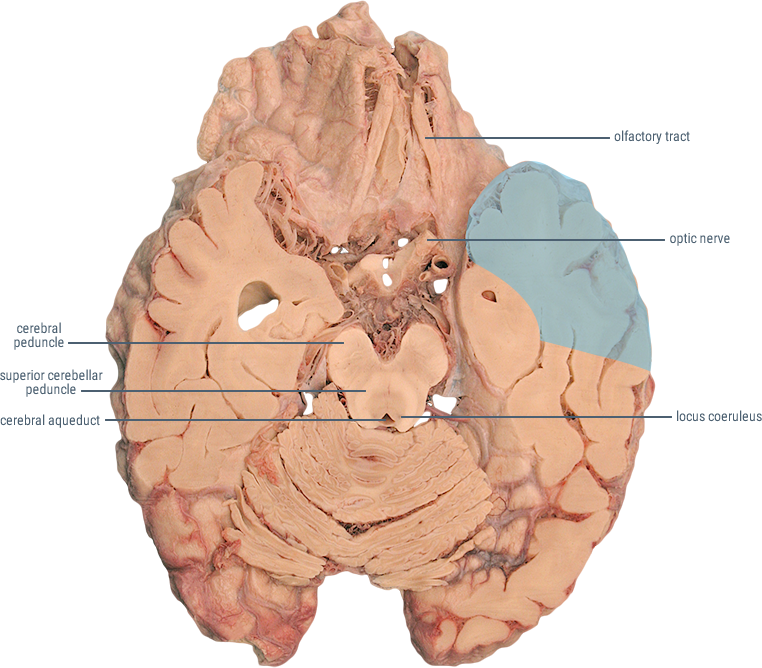
HORIZONTAL SECTIONS
| LOCATION OF INFARCT | DEFICIT |
|---|---|
| Left MCA Superficial Division |
Right face and arm upper motor weakness due to damage to motor cortex, expressive (Broca’s) aphasia due to damage to Broca’s area. There may also be right face and arm cortical-type sensory loss if the infarct involves the sensory cortex. Other deficits include receptive (Wernicke’s) aphasia due to damage to Wernicke’s area. |
| Right MCA Superficial Division |
Left face and arm upper motor weakness due to damage to motor cortex. Left hemineglect (variable) due to damage to non-dominant association areas. There may also be left face and arm cortical type sensory loss if the infarct involves the sensory cortex. |
| Left MCA Lenticulostriate Branches |
Right pure upper motor hemiparesis due to damage to the basal ganglia (globus pallidus and striatum) and the genu of the internal capsule on the left side. Larger infarcts extending to the cortex may produce cortical deficits such as aphasia. |
| Right MCA Lenticulostriate Branches |
Left pure upper motor hemiparesis due to damage to the basal ganglia (globus pallidus and striatum) and the genu of the internal capsule on the right side. Larger infarcts extending to the cortex may produce cortical deficits such as aphasia. |