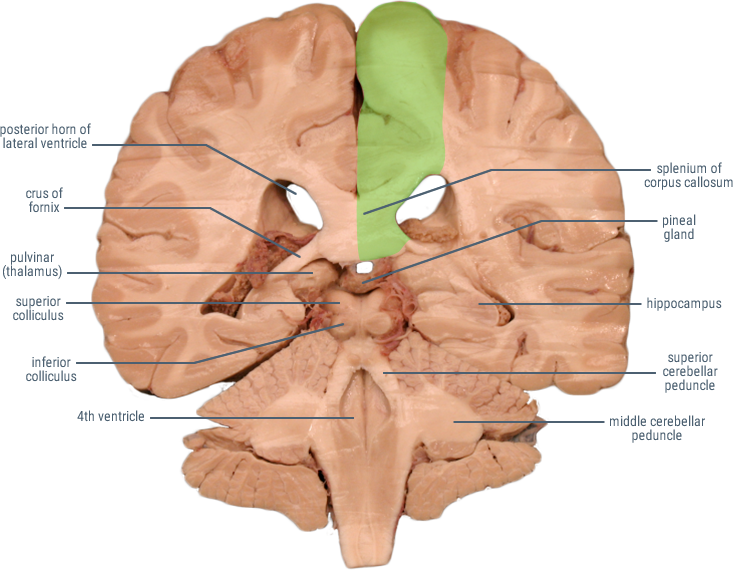
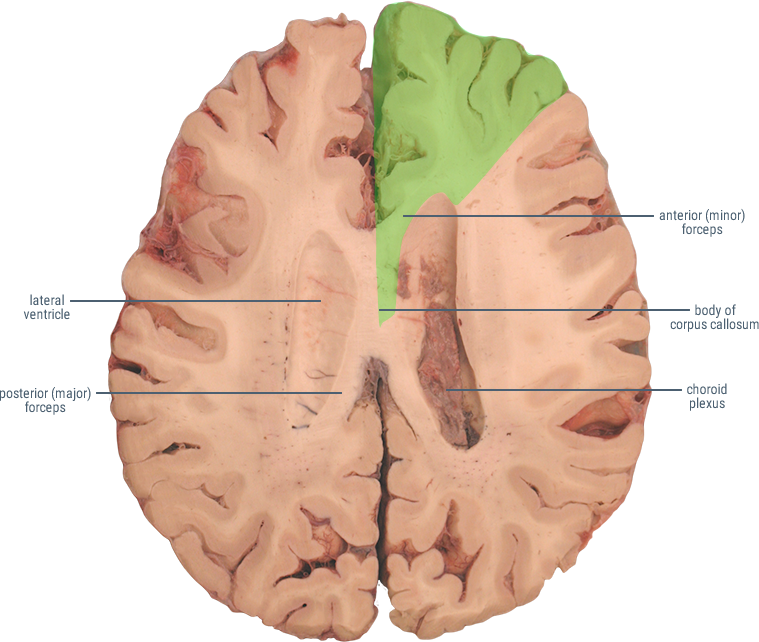
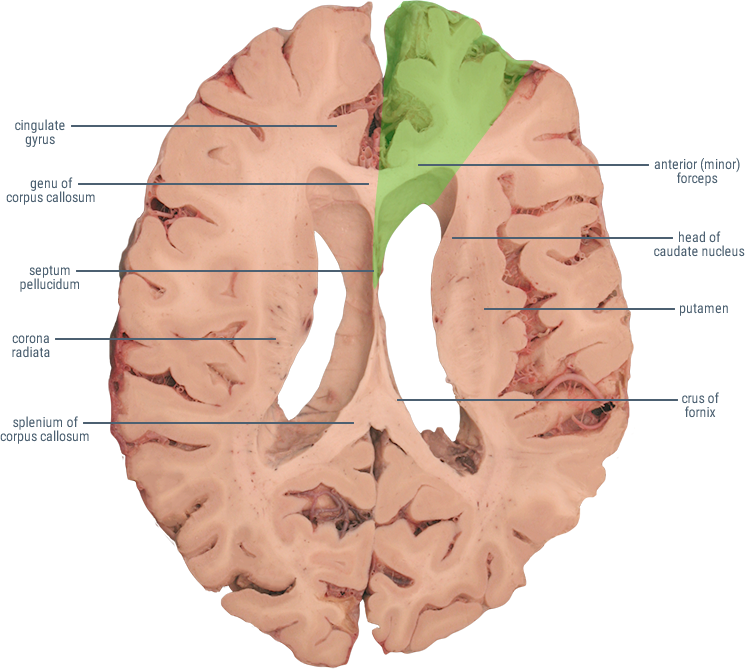
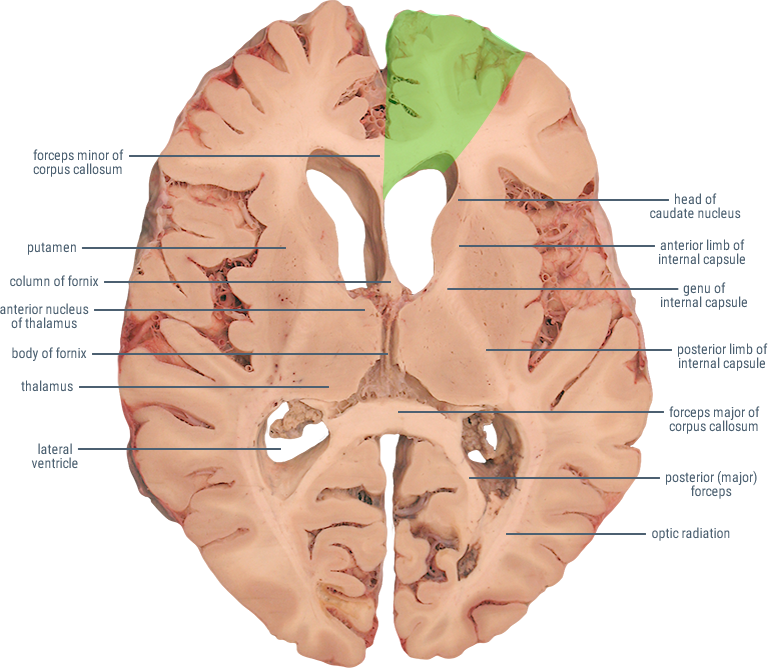
The Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA) supplies the frontal, pre-frontal and supplementary motor cortex, as well as parts of the primary motor and primary sensory cortex. ACA infarcts are rare because of the collateral circulation provided by the anterior communicating artery.
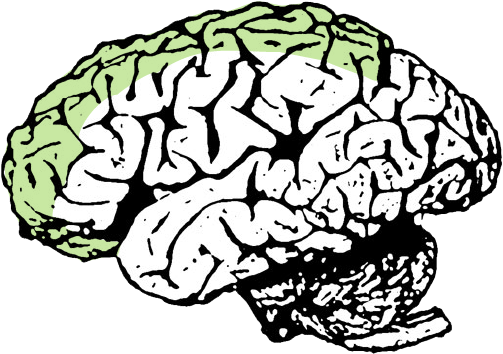
MOTOR CORTEX
(Lower Limb)
(Lower Limb)

Controls movement of the contralateral lower limb.
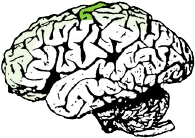
SENSORY CORTEX
(Lower Limb)
(Lower Limb)

Receives sensory input from the contralateral lower limb.
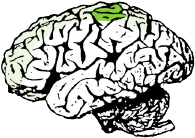
SUPPLEMENTAL MOTOR AREA
(Dominant Hemisphere)
(Dominant Hemisphere)

Functions with Broca’s area in the initiation of speech.
PREFRONTAL CORTEX
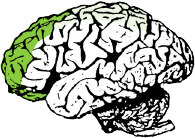

Functions in volition, motivation, and planning and organizing of complex behaviour.
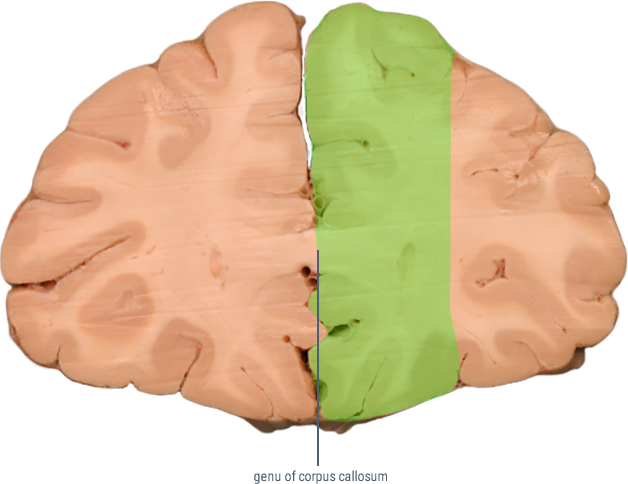
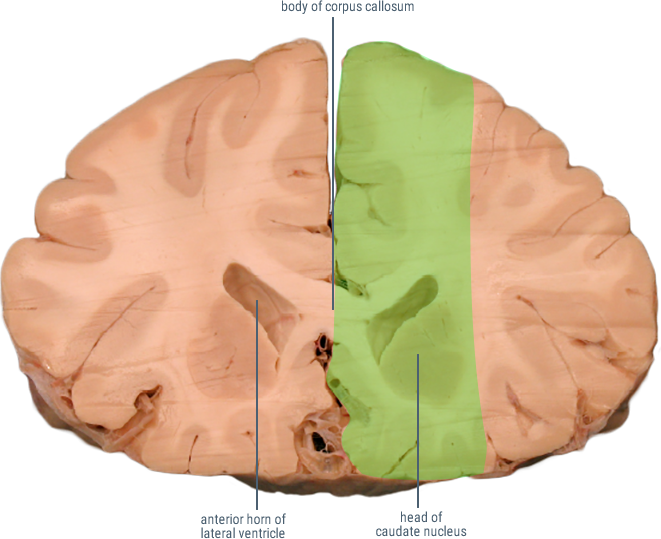
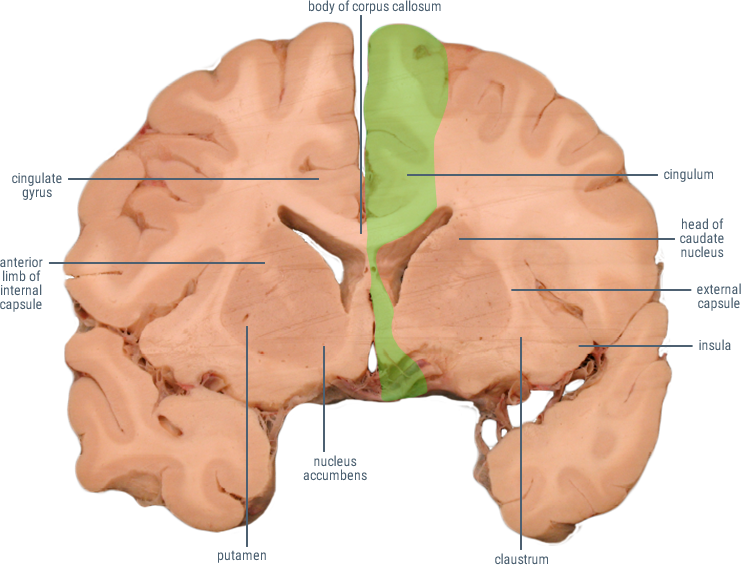
CORONAL SECTIONS
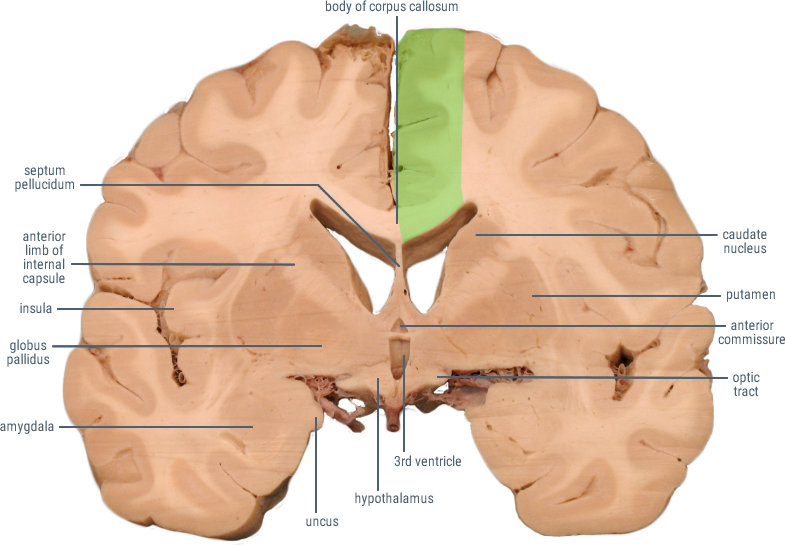
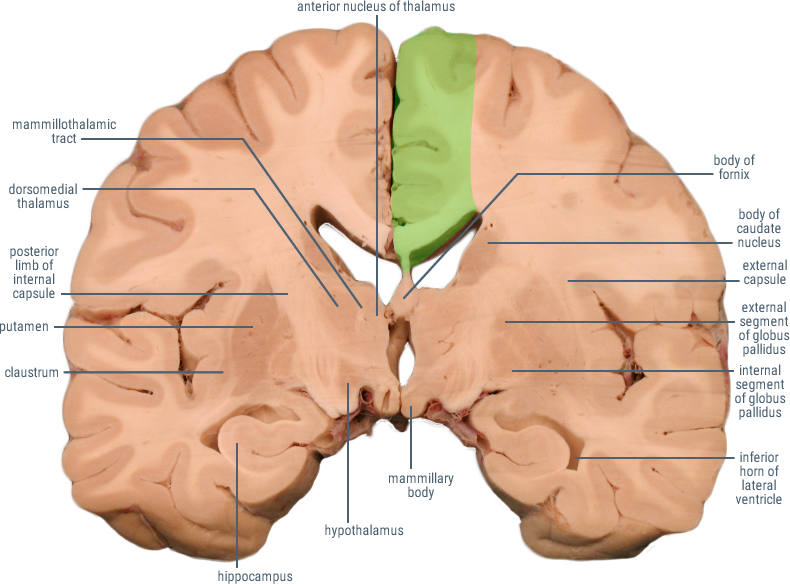
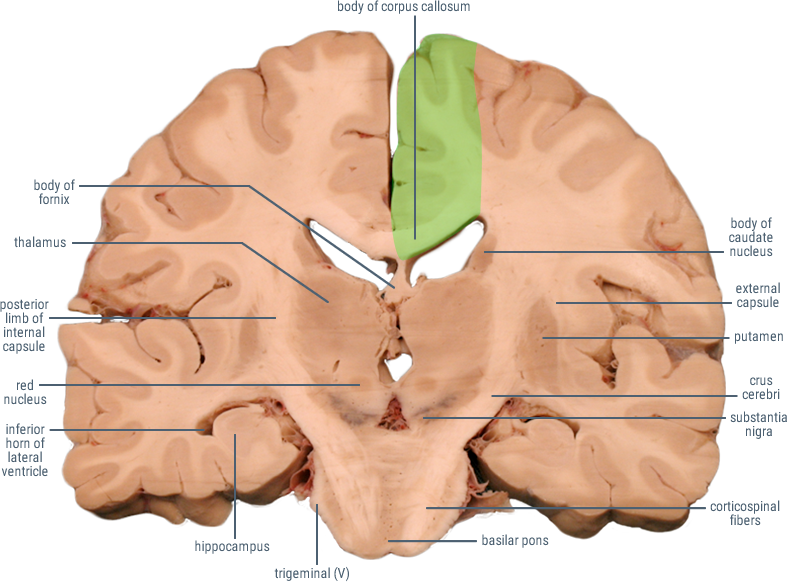
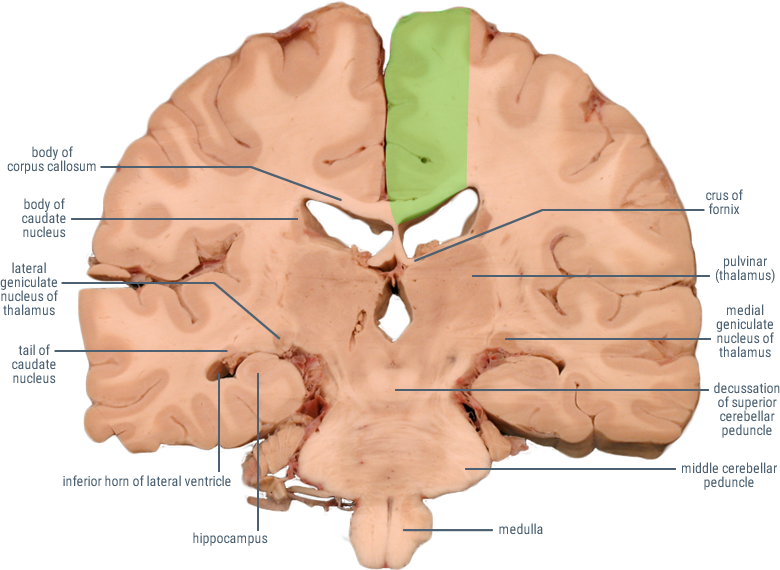
HORIZONTAL SECTIONS
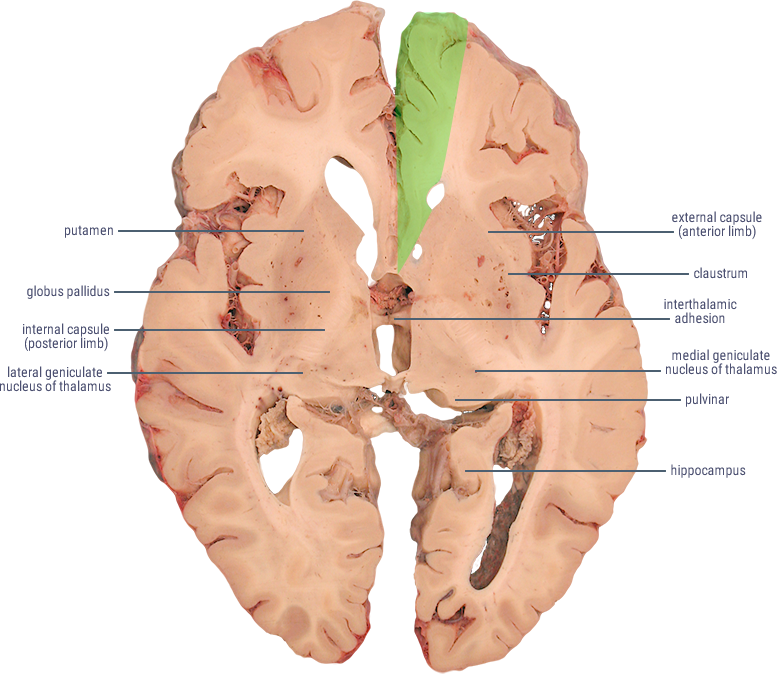
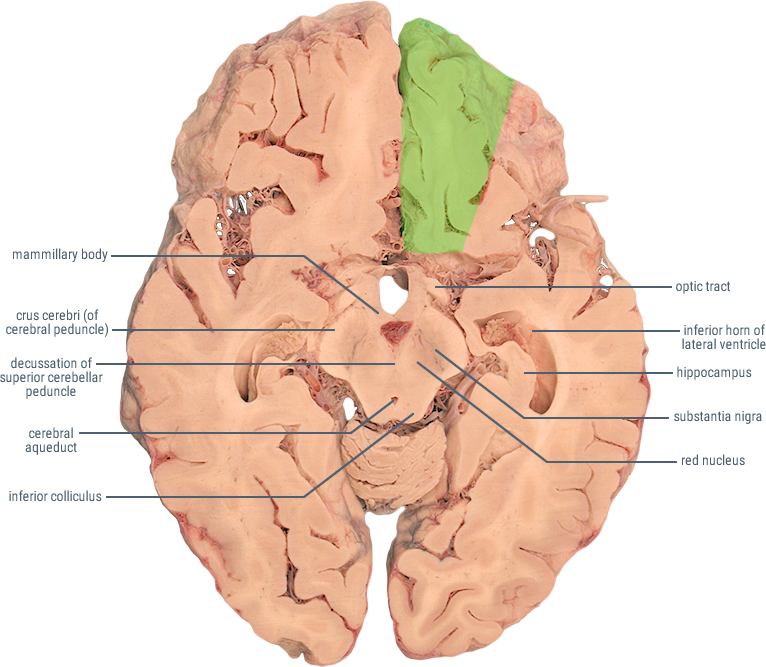
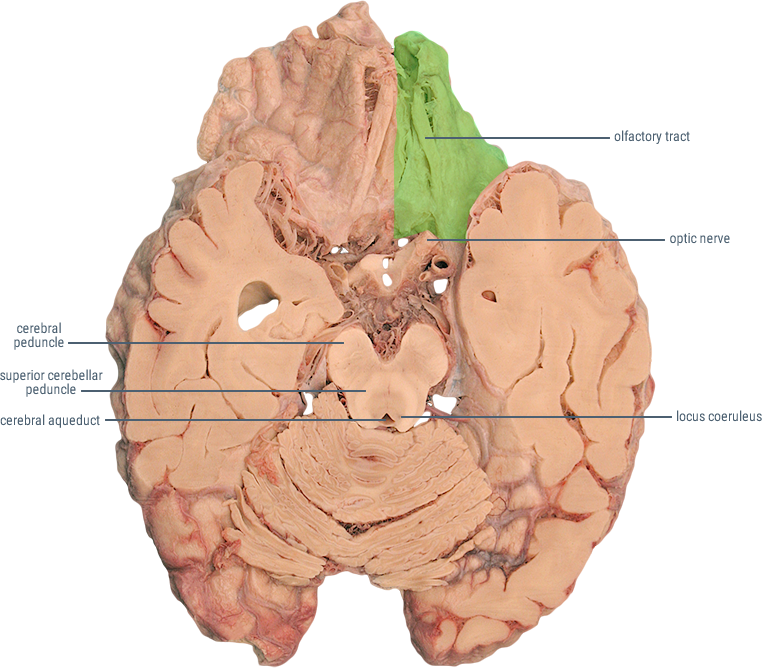
| LOCATION OF INFARCT | DEFICIT |
|---|---|
| Left ACA | Right leg upper motor neuron weakness due to damage to motor cortex and right leg cortical sensory loss due to damage to sensory cortex. Grasp reflex, frontal lobe behavioral abnormalities, and transcortical aphasia can also be seen if the prefrontal cortex and supplemental motor areas are involved. |
| Right ACA | Left leg upper motor neuron weakness due to damage to motor cortex and left leg cortical type sensory loss due to damage to sensory cortex. Grasp reflex, frontal lobe behavioural abnormalities and left hemineglect can also be seen if the prefrontal cortex and non-dominant association cortex are involved. |